304: is a general purpose stainless steel widely used in the production of equipment and parts that require a good combination of properties (corrosion resistance and formability).
301: Stainless steel shows obvious work hardening phenomenon during deformation, and is used in various occasions requiring higher strength.
302: Stainless steel is essentially a variant of 304 stainless steel with higher carbon content and can be made by cold rolling for higher strength.
302B: It is a stainless steel with high silicon content and has high temperature oxidation resistance.
303 and 303SE: Free-cutting stainless steels containing sulfur and selenium, respectively, for applications requiring free-cutting and high luminous brightness. 303SE stainless steel is also used for parts that require hot heading because of its good hot workability under such conditions.
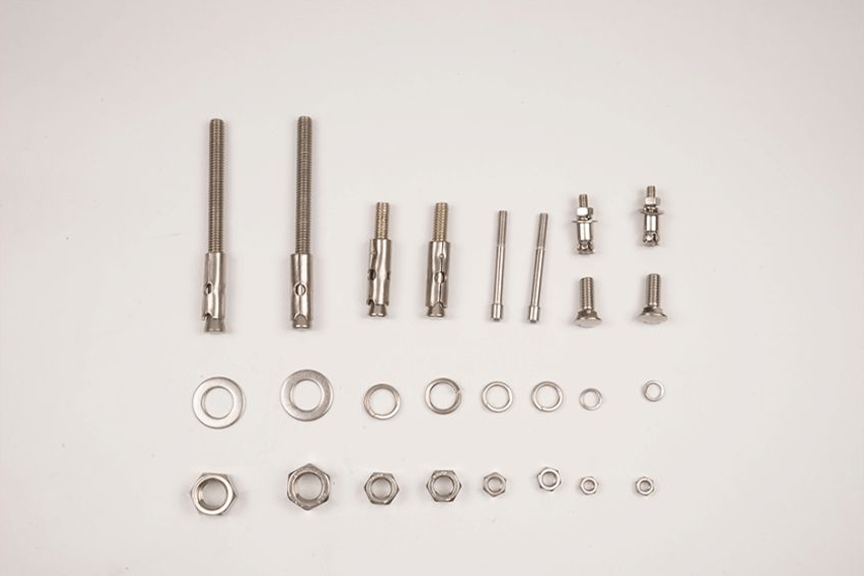
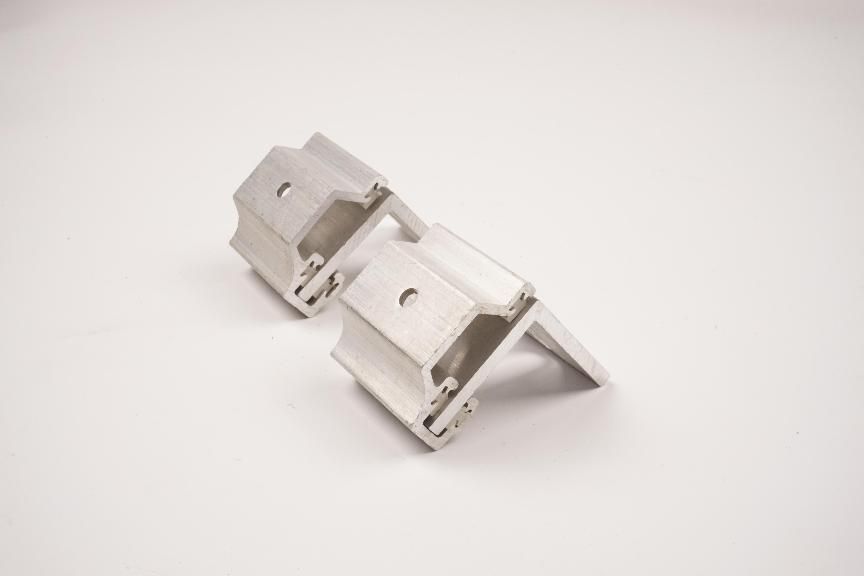


304L: A variant of 304 stainless steel with a lower carbon content for welding applications. The lower carbon content minimizes carbide precipitation in the heat-affected zone near the weld, which can lead to an intergranular corrosion (weld attack) environment in stainless steel in some cases.
04N: It is a nitrogen-containing stainless steel. Nitrogen is added to improve the strength of the steel.
305 and 384: Stainless steel has high nickel content and low work hardening rate, and is suitable for various occasions with high requirements for cold forming.
308: Stainless steel is used to make electrodes.
309, 310, 314, and 330: The high nickel and chromium content of stainless steel increases the steel's oxidation resistance and creep strength at elevated temperatures. While 30S5 and 310S are variants of 309 and 310 stainless steel, the only difference is the lower carbon content, which minimizes carbide precipitation near the weld. 330 stainless steel has a particularly high resistance to carburization and thermal shock.
Types 316 and 317: Stainless steel contains aluminum, so its resistance to pitting corrosion in marine and chemical industry environments is much better than 304 stainless steel. Among them, the varieties of 316 stainless steel include low carbon stainless steel 316L, nitrogen-containing high-strength stainless steel 316N and sulfur content of high-cutting stainless steel 316F.
321, 347 and 348 are titanium, niobium and tantalum, niobium stabilized stainless steels, respectively. They are suitable for high temperature soldering. 348 is a stainless steel suitable for the nuclear power industry. The amount of tantalum and the amount of drilled holes are limited.
The induction coil and the part connected to the welding tongs should be placed reliably to prevent the arc from hitting the steel pipe during operation.
Post time: Jun-03-2019